Introduction To Computer Vision
Computer vision is the ability of artificial intelligence (AI) systems to perform tasks in the same manner as human vision. This includes “seeing” and understanding the visual information. With deep learning algorithms and artificial neural networks, computer vision can substitute human vision.
In recent years, the computer vision field has been taking great strides and can match humans in certain tasks relating to the identification and labelling of objects. The technology has also become increasingly common in various industries.
Images and videos have become one of AI’s most amazing data, which is one of the driving forces behind the growth of computer vision. This is why the global computer vision market is anticipated to reach over USD 48 billion by 2023.
History Of Computer Vision
Computer vision is the field of artificial intelligence that teaches computers to interpret and understand visual information from the world. Here’s a quick look at its evolution:
-
1950s-1960s: The early ideas of computer vision emerged with researchers like Larry Roberts, who began exploring how machines could “see” and interpret images, inspired by human vision.
-
1970s: The development of basic algorithms for image processing, such as edge detection, started to shape the field, but it was still very experimental.
-
1980s: Machine learning techniques began to influence computer vision, helping computers identify patterns and features within images.
-
1990s: Advances in 3D vision and motion analysis helped computers track objects, though the complexity of real-world vision tasks posed challenges.
-
2000s-Present: The big leap came with the rise of deep learning. In 2010, the ImageNet data set became available, containing millions of tagged images across a thousand object classes and providing a foundation for convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and deep learning models used today. In 2012, the breakthrough AlexNet neural network revolutionized image recognition by outperforming previous methods. Since then, deep learning has been used for everything from autonomous driving to medical imaging and facial recognition.

How Does Computer Vision Work?
Computer vision uses deep learning algorithms and artificial neural networks. The particular type of neural network used is called convolutional neural network (CNN) and it helps the system to process images.
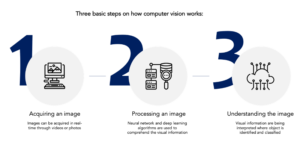
We upload thousands of images to the system to train the neural network. This is to aid the algorithms to comprehend and break down every object that is in the image. The model will scan the images pixel by pixel to recognise patterns and retain them. This retained information can then be used as a reference when scanning other images. With more input, the model will also become smarter and better in providing the right output.
The 5 Computer Vision Techniques

1. Image Classification
Experts have come up with a data-driven approach where computers can interpret and classify images into distinct classes. To do this, the system is provided with various samples of each image class and applies learning algorithms. The computer will then process the visual information of each class.
Classification is the process of locating and classifying a single dominant object in an image. The model will then return a binary value as a yes or no. In the above example, that will be identifying whether the object is a cat or not.
2. Image Classification With Localization
Image classification with localization is the process of allocating a class tag and showing the object by a bounding box. In simple words, it is to draw a box around the specific object.
3. Object Detection
Unlike image classification, object detection can locate and classify many objects in an image. The system is adept in recognizing and locating different objects in an image. Hence, we use object detection in cases where the image cannot be described with a single classification. In this instance, the model can identify the cat and dog and return with the tags accordingly, e.g., red-cat, blue-dog.
4. Object Segmentation
Object segmentation is the process of distinguishing the whole image into groups of pixels. This is to aid the system in determining and classifying the role of each pixel. The model will have to outline each object, e.g., is this pixel a car, a person, a signboard, etc.
In simpler words, instead of just a classification output, object segmentation aims to create and train a neural network that outputs an entire image. Therefore, the model has to provide dense pixel-wise predictions.

Source: Christos Kyrkou
5. Object Tracking
Object tracking is the process of tracking a specific object of interest in images or videos. We often use it in videos where we can track objects from one frame to another. In this example, computer vision is being used to track pedestrians and vehicles.
![]()
Source: The Startup
What Can Computer Vision Do?
1. Image Captioning

Image captioning is the process of extracting textual information from an image. It has various applications like image indexing, for visually impaired people, usage in virtual assistants etc.
2. Facial Recognition

Computer vision is also adept in matching images of people’s faces to their identities. The algorithms will identify the unique facial features and compare them with the database. The system will then determine if the facial features are matched with any image in the database.
Social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram use deep learning algorithms to classify the image elements that users share. For instance, Facebook algorithms can identify people in the uploaded picture based on their facial features and then offer suggestions to tag the person’s account. Additionally, the algorithm can also differentiate humans from objects and animals. For example, Instagram or Snapchat users can use filters, e.g., dog filters, to get a dog face on.
Last but not least, we often use computer vision in our daily lives where we unlock our smartphones using our faces.
3. Body Recognition
The world has been suffering from the COVID-19 pandemic in the past few months. In such circumstances, computer vision technology also plays a critical role. It can perform body recognition and track individuals in any area to see if they are complying with social distancing rules.
As we mentioned previously, computer vision can perform object detection and track them in real-time. Every person in the video will be detected using a green bounding box. Then, the system will track the movement of each box and compute the distance between them. Should the system detect any social distancing violations, the bounding boxes will be highlighted in red.

Source: PyImageSearch
4. Defect Detection
The technology is also capable of detecting defects such as paint defects, bad prints, cracks in meals, etc. This is especially useful in conducting quality checks in the manufacturing industry. It can also be used in identifying defects when constructing buildings. This enables you to take action promptly and rectify these mistakes at an early stage.
Limitations Of Computer Vision
-
Data Dependency: It requires large, high-quality data to work effectively, and poor data can lead to inaccurate results.
-
Environmental Sensitivity: Factors like lighting, weather, and occlusions can impact performance, especially in dynamic environments.
-
Lack of Context Understanding: While it can identify objects, it struggles to understand context or meaning in complex scenes.
-
Bias and Fairness: If training data isn’t diverse, computer vision systems may be biased, leading to inaccurate results for certain groups.
-
High Costs: Developing and maintaining these systems can be resource-intensive and expensive.
Summary
In summary, this article aims to help you have a better understanding of computer vision techniques. The above-mentioned applications are only a few examples of what computer vision can do. There are still many other ways to apply computer vision, for instance,
- Medical Check-Up
- Traffic Surveillance
- Identifying Criminals in Videos, etc.
Here at groundup.ai, we have extensive expertise in the field of AI and computer vision. If you are interested in finding out how computer vision can help you, feel free to Contact us!












